The measure of electric pressure is a Volt (V), Named after Alessandro Volta

Current is measured in Amps ( I ), Named after André Ampere
Power in a DC circuit is Volts x Amps V x I = Power (Watts)
Closing a switch joins the contacts together and lets the current flow through.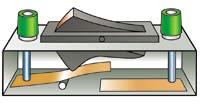
In this simple circuit closing the switch makes the lamp light up because the battery can push an electric current around the circuit.
Suppose a circuit has a 50 volt battery and the current flowing in the circuit is 2 amps, then the power in this circuit is:
W (watts) = V (Volts) x I (Amps) = 50 x 2 = 100 Watts 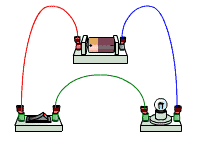
In other words, for maximum brightness the lamp must have 100 Watts of power
Our homes, offices and factories are powered through the benefit of AC current, as opposed to direct current (DC), which is used in batteries. The use of this type of current instead of DC current is predominantly due of issues involving cost, power loss, and conversion issues from higher voltage to lower voltage.
AC currents are created by rotating a magnet inside wire coils that remain still. As one end of the magnet is positive and one is negative, it causes the coils to produce an electric sine wave. The frequency of this wave is 50Hz (cycles per second) for these types of generators.
As the voltage and current waveforms are sinusoidal in AC circuits, so their amplitudes are constantly changing over time. Since we know that power is voltage times the current (P = V*I), maximum power will occur when the two voltage and current waveforms are lined up with each other. That is, their peaks and zero crossover points occur at the same time. When this happens the two waveforms are said to be "in-phase".
A unit of power is a Watt therefore a kilowatt is 1,000 Watts
Our meters measure the power used and the time taken as Kilowatt-hours (kWh)
Therefore: MWh is 1,000 kWh and A GWh is 1,000 MWh
Voltages
As required by law, the electricity delivered to your premises through our distribution system will normally be at one of the voltages set out below and will have the technical characteristics stated there:
At 230 volts nominal: normally a single-phase supply, with a permitted range of voltage variation from plus 10% to minus 6%.
At 400 volts nominal: normally a three-phase supply, with a permitted range of voltage variation from plus 10% to minus 6%.
At either of the above voltages: the supply frequency will be 50 hertz, with a permitted nominal variation of plus or minus 1%.
Electric power distribution is the delivery system of electricity to places that use it, such as homes and other buildings. It is done mainly by power cables, transformers, substations and meters. The electricity comes from the power station at extra high voltage and is delivered at medium to low voltage levels.
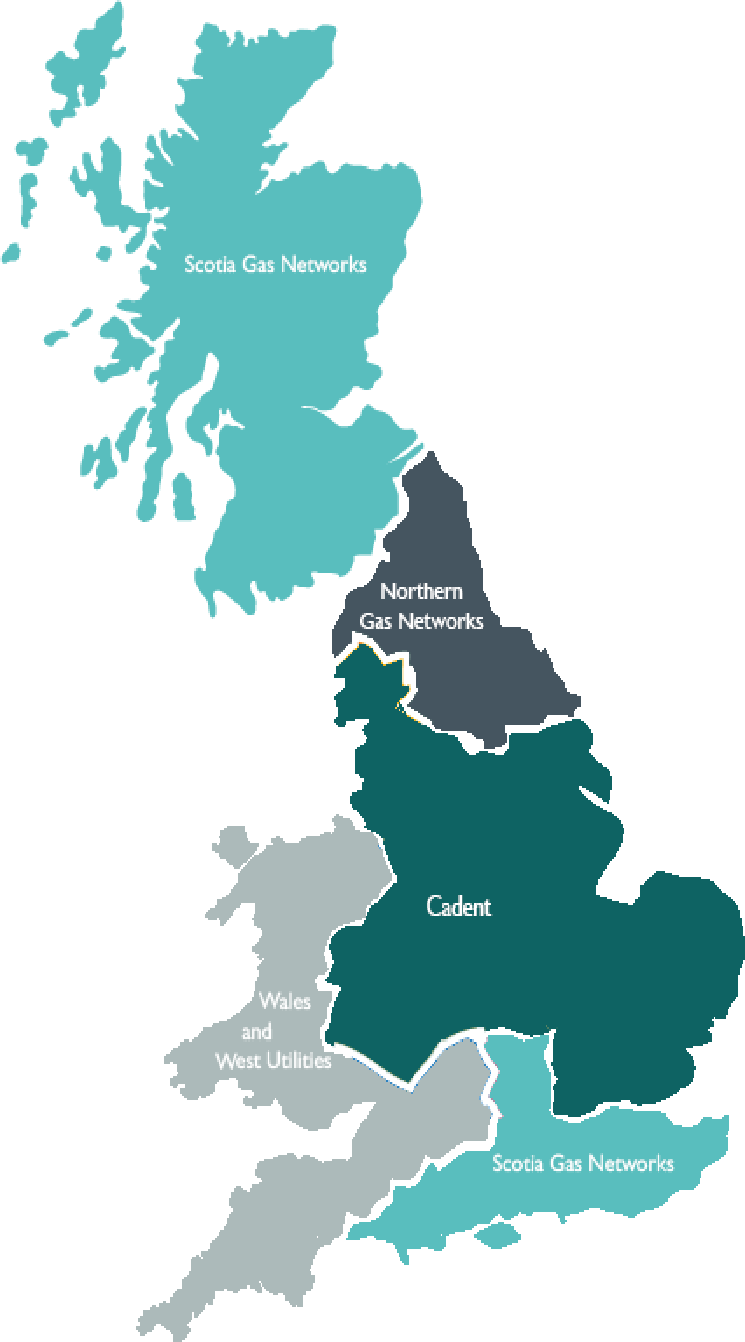
There are 14 licensed distribution network operators (DNOs) in Britain and each is responsible for a regional distribution services area. The 14 DNOs are owned by six different groups.
The DNO groups and individual DNOs are:
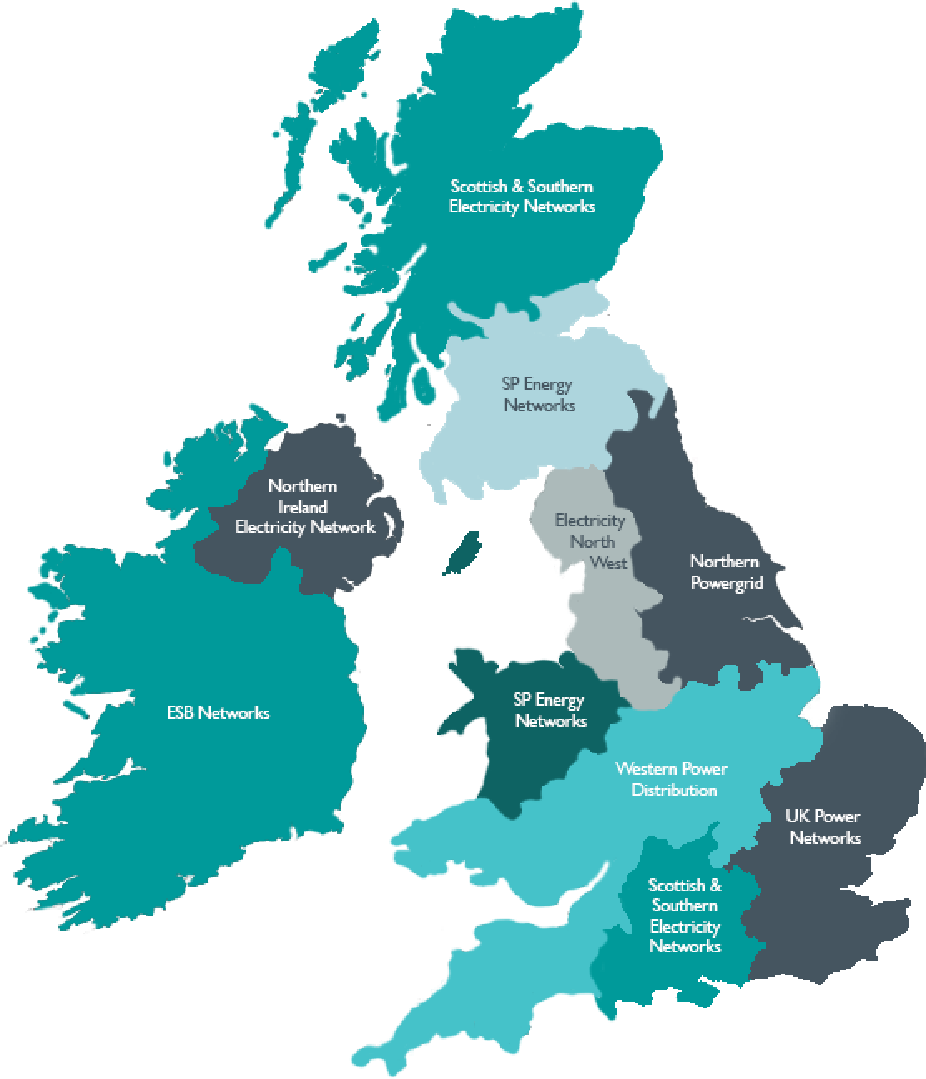
In addition there are also a number of networks owned and operated by Independent Distribution Network Operators (IDNOs). These are located within the areas covered by the DNOs
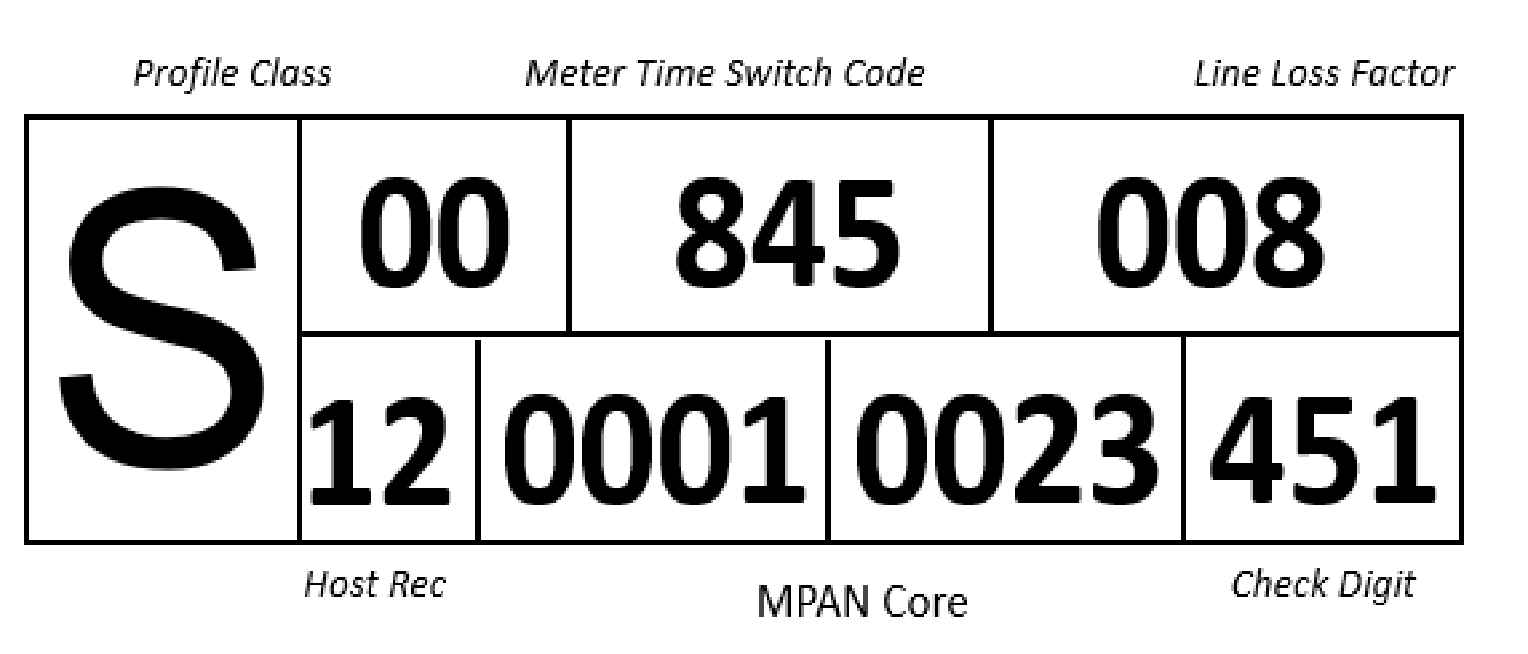
Each meter has it’s own unique MPAN: Meter Point Administration Number
UMS – Unmetered Supplies
Some equipment we supply do not have any meters, e.g. street lights, phone masts, traffic lights, telephone boxes, festive lights etc.
These are UMS or “Un-Metered Supplies”
Why ?
Financially or technically impractical or unsafe to install a meter or carry out meter readings, or because the load is small (less than 500W) and consumption is predictable
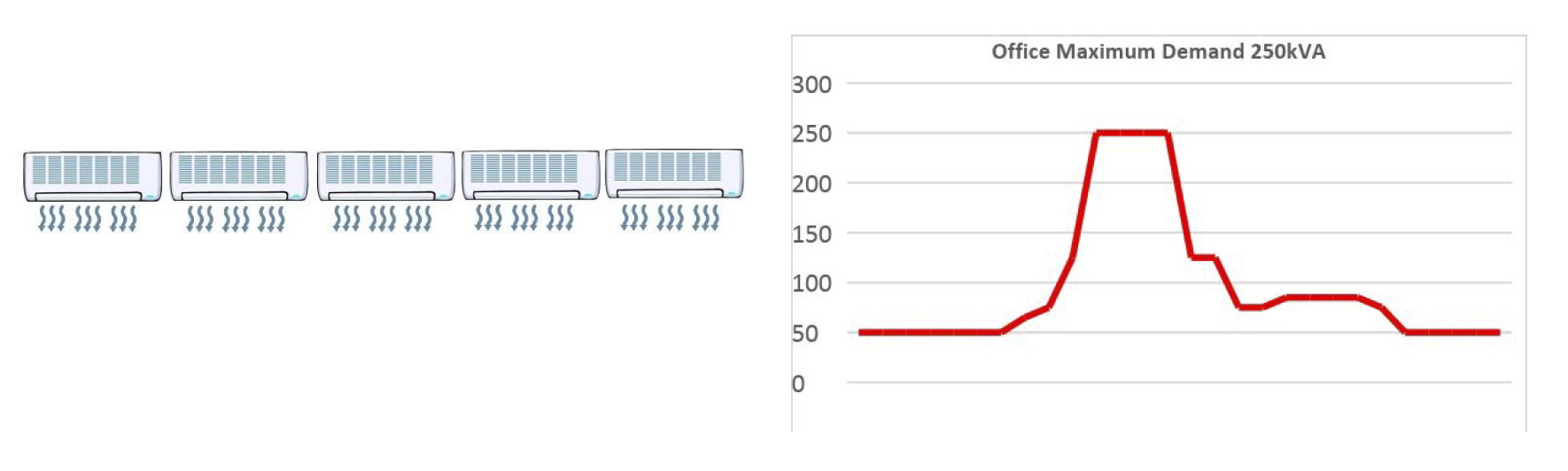
Maximum Demand is the largest consumption of electricity measured in any half hourly period. It is calculated for each calendar month in kVA using the data downloaded from your electricity meter.
For electricity connections above 100Amp three phase, normally a commercial or manufacturing site, meters are installed which allow remote download of the data through the national settlements system each night.
For these types of connections you can appoint your own Meter Operator to install and operator your meter as well as a Data Collector and Data Aggregator to manage the settlements process, alternatively this can be incorporated within the agreement with your chosen electricity supplier.
How Does MD Occur?
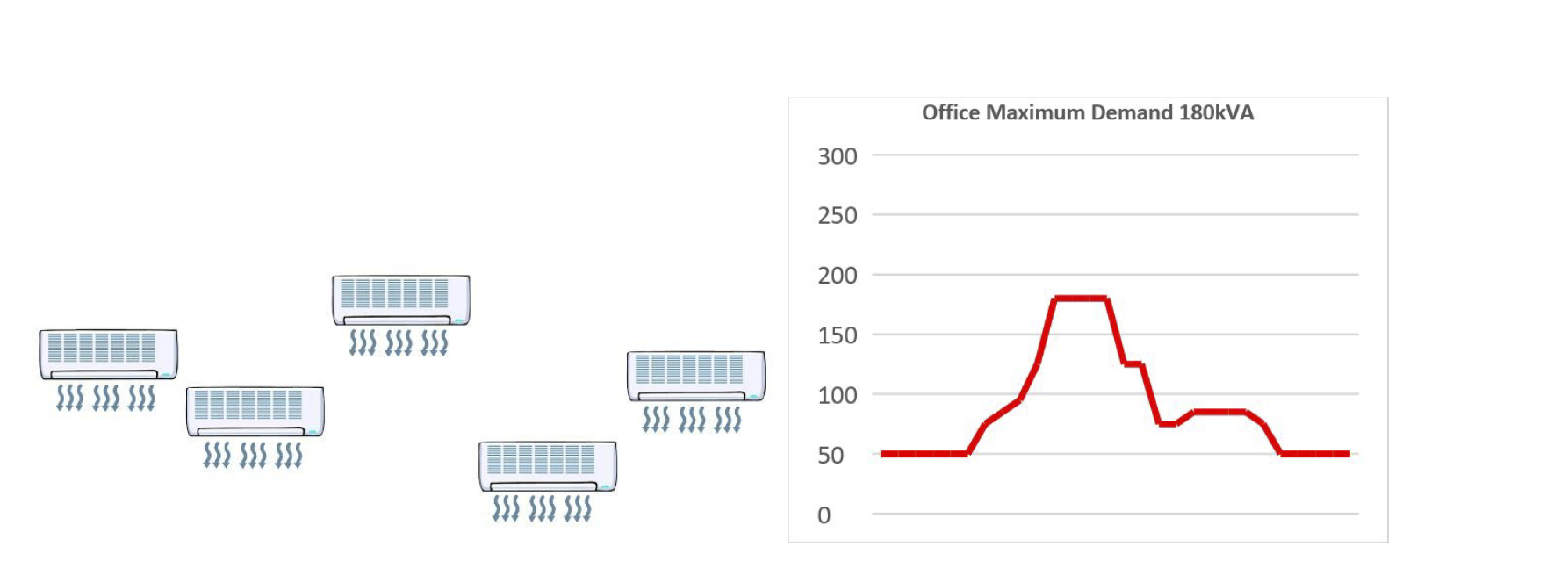
For example, if you switch all your office air conditioning on at the same time and it takes over half an hour to get to the required temperature then this will be the likely cause of your peak maximum demand each day.
Stagger the times the air conditioning is switched on using timers and you can reduce your maximum demand, even though the energy required to get to the temperature is the same this will reduce your Maximum Demand.
What is availability charge?
and affects the type of connection made to your building. At the time of agreeing a contract/supply agreement you will need to confirm the kVA (availability) required.
Customers must restrict their usage to the agreed availability, otherwise they could be penalised at a higher rate for any demand above this level, depending on the published regional distribution charges. If you want to increase your availability it may require a change in the connection arrangement which we would be happy to look into for you.
What is power factor?
Power factor can be considered as the efficiency of electricity usage within a building.
It is the ratio of kW to kVA at the intake position which is determined by the nature of the load being supplied within the premises. The difference is as a result of the phase angle between the current and voltage waveforms. The more motors/rotating machines you have the more inductive the load, this can be corrected by installing a capacitive load in parallel typically using a bank of capacitors, which bring the current and voltage waveforms back in phase with each other.
Gas is distributed in the UK as follows:
Gas Distribution is the supply of gas to homes and industry through mains and services.
Gas Governors
The intermediate pressure and medium pressure gas distribution system is supplied from the high pressure gas transmission system through pressure reduction stations.
Pressure reduction stations usually called gas governors reduce the gas pressure from the intermediate and medium pressure mains into the low pressure distribution system and are designed to ensure that the pressure in the network does not exceed the maximum design pressure.
Gas Mains
Gas mains in the united Kingdom fall into the following types:
- Intermediate pressure mains operating between 2 and 7 bar and constructed from either steel or polyethylene pipe.
- Medium pressure mains operating between 75mbar and 2bar and constructed from either steel, polyethylene, cast iron or ductile iron pipe.
- Low pressure mains operating at approximately 25mbar and up to pressures of 75mbar and constructed of polyethylene, cast iron or ductile iron pipe.
Gas Services
Gas services are smaller diameter pipes, usually up to 63mm diameter which are connected to low, medium or intermediate pressure mains and take gas into homes, commercial or industrial buildings.
A gas service regulator is connected to the end of the service pipe before the gas meter to reduce the gas pressure, usually to 21 mbar to supply gas appliances installed in the premises.
Laying gas mains and services in the highway
Laying gas mains and services in roads and footpaths is controlled by the New Roads and Street Works Act (NRSWA). Companies laying mains in the public highway have to give notice to Local Authorities of their intention to excavate in a road or footpath. They must also provide estimates of the length of time a construction project is going to take to complete. Where projects run over the estimated completion time, Local Authorities are able to levy penalties against offending companies. This is known as Section 74.
Gas on new housing sites
Gas mains and services on new housing sites must be sized so that they can deliver gas to homes at a pressure of approximately 25mbar in the quantities needed to supply all the gas appliances installed in the house. The design of gas mains and services involves a system called Network Analysis. Many of the gas mains and services installed on new housing sites are owned operated and maintained by Licensed Gas Transporters. Licensed Gas Transporters must demonstrate through their Safety Case that their gas networks are fit for purpose and comply with the Health and Safety Executive Gas Safety(Management Regulation).
Licensed Gas Transporters must ensure that organisations contracted to lay gas mains and services undertake the work to industry standards before the mains and services are adopted into their ownership.
The Gas Industry Registration Scheme (GIRS) ensures that Companies undertaking gas mains and service work are competent. The GIRS scheme is operated by Lloyds Register.
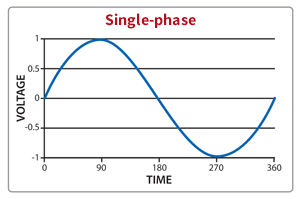
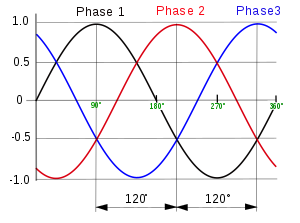
Single phase uses a single ‘live’ conductor plus a neutral. Three phase uses three ‘live’ conductors plus a neutral. Single phase is typically used for domestic small supplies and three phase for larger and commercial supplies. Single phase is one sinusoidal wave and alternates at 50 cycles per second (Hertz) and dips below the x axis half way through a wave. Three phase is made up of three sinusoidal waves at 120° separation, this results in a much smoother overall power supply with each peak leading to the next and not dipping below the x axis.
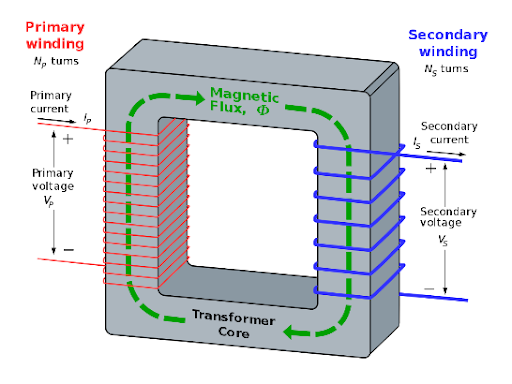
A transformer is an electrical device that is used to increase or decrease voltages. It does this by transferring energy between two circuits by creating a magnetic field in one circuit which induces a current in the second circuit. The two circuits both contain coils and it is the ratio between the number of turns in each coil that dictates the voltages induced in the second circuit.
Depending on where your connection is required there may not be sufficient capacity in the low voltage network. If this is the case a high voltage point of connection may be offered. High voltage electricity cannot be used for small or domestic consumption and so a transformer will be required to reduce this down to usable low voltage.
Accreditations
- NERS - National Electricity Registration Scheme
- WIRS - Water Industry Registration Scheme
- GIRS - Gas Industry Registration Scheme
Bodies of Authority
- OFGEM – Office of Gas and Electric Markets
- IGEM - Institute of Gas Engineers and Managers
- IET – Institution of Engineering and Technology
- ENA – Energy Networks Association
Electric
- ICP – Independent Connection Provider
- DNO – Distribution Network Operator
- IDNO – Independent Distribution Networks Operator
- LS0H – Low Smoke Zero (0) Halogen
- PV – Photo Voltaic
- CHP – Combined Heat and Power
- ELI – Earth Loop Impedance
- PMT – Pole Mounted Transformer
- GRP – Glass Reinforced Plastic
- TX - Transformer
- POC – Point of Connection
- CSEP – Connection System Exit Point
- MSDB – Multi Service Distribution Board
- PME – Protective Multiple Earth
- CNE – Combined Neutral Earth
- SNE – Separate Neutral Earth
- BCA – Bilateral Connection Agreement
- kWh - Kilo Watt Hour
- UMSO – Unmetered Supply Operator
- ECV – Emergency Control Valve
- LV – Low Voltage
- HV – High Voltage
- EHV – Extra High Voltage
- MPAN – Meter Point Administration Number
- SCADA – Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
General Construction
- CSCS – Construction Skills Certifications Scheme
- PPE – Personal Protective Equipment
- CAD – Computer Aided Design
- LA – Local Authority
- FL – Transport for London
- HSE – Health and Safety Executive
- COSHH – Control of Substance Hazardous to Health
- CITB – Construction Industry Training Board
- CDM – Construction, Design and Management Regulations
- NRSWA – New Roads and Street Works Act
- TMA – Traffic Management Act
- GA – General Arrangement
- PO – Purchase Order
- EUS – Energy and Utility Skills
- CPCS – Construction Plant Competence Scheme
- SLD – Single Line Diagram/Drawing
- SCH – Schematic
- I&C – Industrial and Commercial
- MAM – Meter Asset Manager
- OAMI – Ofgem Approved Meter Installer
- PUWER – Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations
- RIDDOR - Reporting of Injuries, Disease and Danger Occurrence Regulation
Gas
- MP – Medium Pressure
- LP – Low Pressure
- IP – Intermediate Pressure
- IGEM - Institute of Gas Engineers and Managers
- MPRN – Meter Point Reference Number
- GNO – Gas Network Operations
- TA – Technical Advisor
- NRO – Non-Routine Operation
- RO – Routine Operation
- CP – Competent Person
- GT – Gas Transporter
- IGT – Independent Gas Transporter
- CSEP – Connection System Exit Point
- PRI – Pressure Reduction Installation
Call us on: 01604 343 970 Or Email us at: info@TheICP.co.uk
Your login details have been used by another user or machine. Login details can only be used once at any one time so you have therefore automatically been logged out. Please contact your sites administrator if you believe this other user or machine has unauthorised access.

